Crew AI – Orchestrate Collaborative AI Agent Teams
Crew AI is a Python framework designed to build and orchestrate autonomous AI agents that collaborate on complex tasks. Developed by João Moura and launched in early 2023, the open-source framework has quickly gained traction, securing $18 million in funding from prominent investors like Insight Partners and AI leaders such as Andrew Ng. It is exceptionally useful for developers and businesses looking to automate intricate, multi-step workflows that are too complex for a single AI model.
The AI Agent platform targets a technical audience, including developers and AI engineers across industries like marketing, finance, and software development. Crew AI’s primary value proposition is its ability to create a “crew” of specialized AI agents that work together, much like a human team. Each agent has a defined role, its own set of tools, and can delegate tasks to other agents. This approach disrupts traditional, manual workflows by dividing and conquering complex problems, enabling a level of automation and efficiency that was previously difficult to achieve with single-agent systems.
Best Use Cases for Crew AI
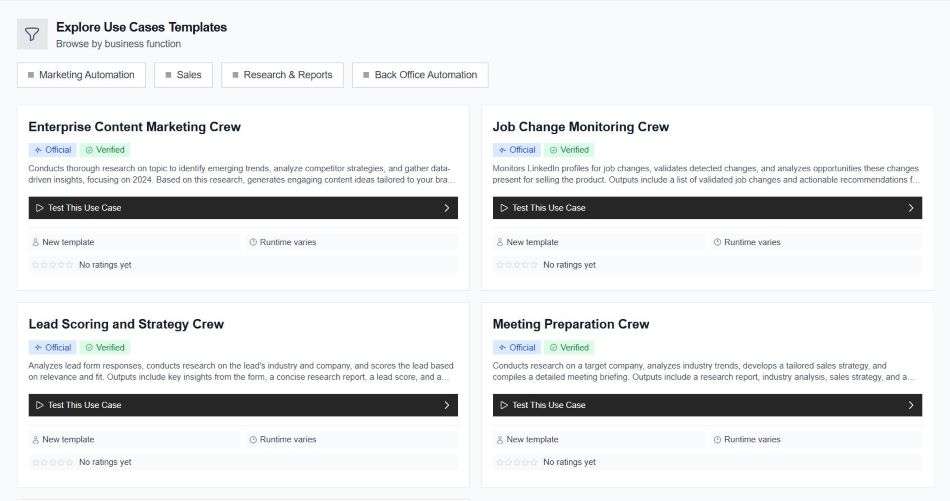
- Marketing Professionals: Imagine creating a complete marketing campaign without manual intervention. A “Content Creation Crew” can be assembled where one agent researches trending topics, another writes a detailed blog post, a third agent creates corresponding social media snippets, and a fourth analyzes the campaign’s performance data. This solves the problem of siloed, time-consuming content workflows.
- Sales Teams: Crew AI can automate the entire top-of-funnel sales process. A crew can be designed to have a “Lead Scraper” agent identify potential customers from online sources, a “Prospect Qualifier” agent enrich that data and score leads, and an “Outreach Specialist” agent draft personalized cold emails, freeing up human sales reps to focus on closing deals.
- Software Developers: In a development setting, Crew AI can significantly accelerate a project’s lifecycle. You could build a “DevOps Crew” where one agent writes unit tests for new code, another agent attempts to debug and fix failing tests, and a third agent summarizes the results and prepares a report for human review. This automates repetitive coding and testing tasks.
- Financial Analysts: A financial services firm can deploy a crew for market research and analysis. An “Analyst Agent” can be tasked with gathering quarterly earnings reports from various companies, a “Data Processing Agent” can extract key metrics, and a “Reporting Agent” can compile the findings into a structured, easy-to-read summary for investment strategists.
Powerful Collaborative Framework: Crew AI’s core strength is enabling multiple AI agents to work together, delegate tasks, and share information to solve complex problems.
Role-Based Agent Design: The ability to define specific roles, goals, and backstories for each agent makes the development process intuitive.
Flexible LLM Integration: Developers can easily plug in different models from providers like OpenAI, Google, or open-source alternatives.
Customizable Toolsets: Agents can be equipped with any number of custom tools, including search functions, APIs, or proprietary databases.
Human-in-the-Loop: Workflows are not fully autonomous by default. The framework allows for human oversight and approval, which is critical for sensitive tasks.
Open-Source Core: The main Crew AI framework is open-source, fostering a strong community and allowing for high levels of customization and transparency.
Scalable Task Execution: The system supports both sequential and parallel task execution, allowing for efficient workflows that can scale with complexity.
Requires Python Expertise: This is a developer's tool. A solid understanding of Python is necessary to build and manage crews, making it inaccessible to non-technical users.
Opaque Enterprise Pricing: While a free tier exists, the pricing for the Pro and Enterprise plans is not fully transparent and can reportedly become very expensive.
Steep Learning Curve for Beginners: Debugging complex interactions between multiple agents can be challenging for those new to the framework.
Lacks Mainstream Business Reviews: Absence of user reviews on major software review platforms like G2, Capterra, or Trustpilot, which can be a red flag for business buyers.
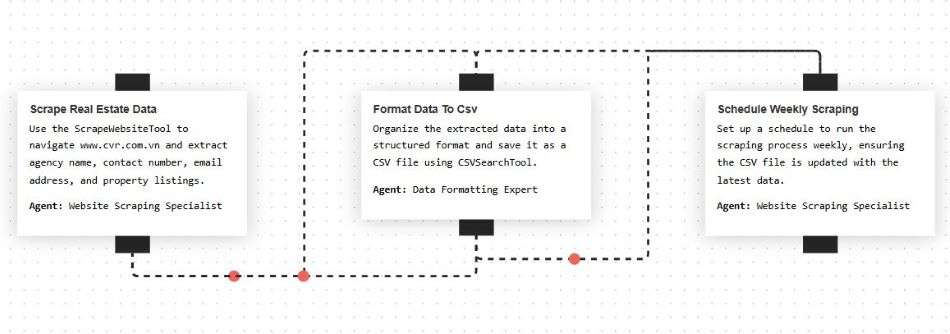
- Role-Based Agents: Create agents with specialized functions, goals, and backstories to guide their behavior.
- Autonomous Delegation: Agents can intelligently delegate tasks to other agents within the crew without human intervention.
- Custom Tools: Equip agents with a wide array of tools, from simple search functions to complex API integrations.
- Task Management: Define tasks with clear descriptions and expected outputs for agents to execute.
- Crew Orchestration: Assemble agents and tasks into a cohesive crew that works together to achieve a final objective.
- Sequential Task Execution: Run tasks one after another, ensuring a logical progression for linear workflows.
- Parallel Task Execution: Allow agents to perform tasks simultaneously for increased speed and efficiency.
- Flows: Build more structured, event-driven workflows for fine-grained control over agent interactions.
- Human Input: The ability for humans to provide input during the process, guiding the crew’s work.
- LLM Agnostic: Compatible with various Large Language Models, giving developers the freedom to choose the best model for their needs.
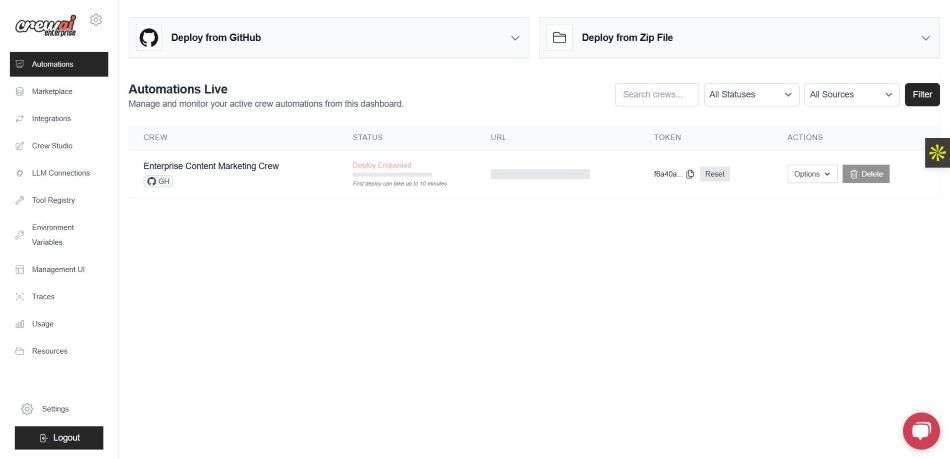
- Cloud & Self-Hosted Deployment: Offers flexibility in deployment, with options for using the Crew AI cloud platform or self-hosting.
 crew-ai-dashboard
crew-ai-dashboard
 Deployment
Deployment
 Deploy-stage
Deploy-stage
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is Crew AI?
Crew AI is an open-source Python framework that enables developers to build and manage teams of autonomous AI agents that collaborate to complete complex tasks. -
Who is Crew AI for?
Crew AI is primarily for Python developers, AI engineers, and businesses that have technical teams capable of building custom AI-powered workflows. -
How much does Crew AI cost?
Crew AI offers a free tier with 50 executions per month. Its Pro plan starts at $99.99 per month, and it also offers a custom-priced Enterprise plan. -
What skills are needed to use Crew AI?
A user must have a strong working knowledge of Python to effectively use the Crew AI framework to build and manage agents. -
How is Crew AI different from LangChain?
LangChain is a general-purpose framework for building LLM applications, whereas Crew AI is a specialized framework built on top of LangChain specifically for orchestrating multi-agent collaboration. -
Can Crew AI agents browse the internet?
Yes, agents can be equipped with tools, such as a search tool, that allow them to access and browse the internet for information. -
Is Crew AI open source?
Yes, the core framework of Crew AI is open-source and available on GitHub, while the company also offers a managed cloud platform with additional features.
Tech Pilot’s Verdict on Crew AI
As an AI tool reviewer, I’ve seen countless platforms promise to revolutionize workflows, but Crew AI’s approach feels both practical and powerful. My goal was to assess if its collaborative agent framework truly delivers on its promise of automating complex tasks. I didn’t run code myself, but I dove deep into its documentation, community discussions, and user-built examples to understand its real-world capabilities.
I started by conceptualizing a “Market Research Crew.” The mission: analyze the emerging trend of AI-native hardware devices. I envisioned a crew with a “Researcher Agent” to scour the web for articles and product launches, a “Synthesizer Agent” to distill the key findings and market players, and a “Writer Agent” to draft a summary report. What immediately stood out was the intuitiveness of this role-based system. Defining an agent’s role, goal, and backstory provides a clear and powerful way to constrain the LLM’s behavior, which is a common challenge in AI development. The ability to assign specific tools—like a search API for the researcher—is where the magic happens. This is not a theoretical exercise; it’s a tangible way to build a functional, automated team.
However, the reality of implementation isn’t all plug-and-play. Watching tutorials and reading through developer forums, it’s clear that while simple crews are easy to set up, debugging the interactions in a complex, multi-agent system can become a headache. When an agent fails to pass information correctly or gets stuck in a loop, pinpointing the issue requires real Python debugging skills. This is the trade-off for its power and reinforces that Crew AI is a tool for developers, not a no-code solution for the average business user.
The pricing model is another point of friction. The free tier is not enough for experimentation, and the leap to paid plans is very steep with not many generations available, unless you are willing to spend 10.000$ per month. For a startup or small business, the potential for costs to escalate based on execution volume is a significant factor to consider. You’re not just paying for Crew AI; you’re also paying for the underlying LLM API calls, which can add up quickly.
Top Alternatives to Crew AI
When considering Crew AI, it’s essential to look at its main competitors, as each serves a slightly different purpose.
-
AutoGen: Developed by Microsoft Research, AutoGen is a highly flexible framework for creating complex multi-agent conversations. Unlike Crew AI’s more structured approach, AutoGen excels at open-ended problem-solving where agents dynamically define the path forward. It is more of a research tool and has a steeper learning curve than Crew AI. AutoGen is a better choice for users tackling novel, unpredictable problems that require emergent agent behaviors.
-
LangChain: LangChain is the foundational “Swiss Army knife” for building LLM applications; in fact, Crew AI is built using it. LangChain provides all the components you could possibly need, but you have to assemble them yourself. It is more versatile than Crew AI but also more complex for the specific task of agent orchestration. If you need to build a simple, single-agent application or a highly customized LLM workflow that goes beyond agent collaboration, LangChain is the more appropriate tool.
-
Lyzr: Lyzr positions itself as a more enterprise-ready agent framework with a focus on security, reliability, and faster development cycles using SDKs. It offers a broader range of pre-built agent types (e.g., for data analysis, chatbots) compared to Crew AI’s more DIY approach. While both target businesses, Lyzr is designed for enterprises that need to deploy production-grade agents with robust support and less custom coding. Its weakness is that it is less flexible and community-driven than Crew AI.
For structured, repeatable business automation, Crew AI offers the best balance of power and usability. For pure research and complex, unpredictable problem-solving, AutoGen is superior. For foundational, highly custom LLM application development, LangChain is the go-to choice.
In conclusion, my verdict is that Crew AI is a category-defining tool that brilliantly executes the concept of collaborative AI. It provides a robust, organized, and powerful framework for developers to automate sophisticated workflows. It’s not a simple tool for a non-technical person, and the costs can be a concern. However, for a business with the right technical talent, Crew AI can unlock a new level of operational efficiency and is one of the most exciting AI tools on the market today.

